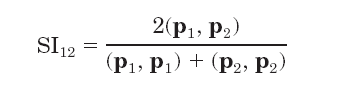
Molecular electrostatic potentials can be compared quantitatively by calculating similarity indices. Similarity indices have been developed for, and are usually applied to, the comparison of small molecules. They are, however, also useful for the analysis of macromolecules, allowing classification as well as prediction of the functional properties and active sites of macromolecules. The Hodgkin index is commonly used to measure the similarity of two molecular potentials. It detects differences in sign, magnitude, and spatial behavior in the potentials and is given by
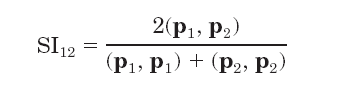
If the electrostatic potentials 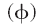 are computed on a three-dimensional grid over the two superimposed
molecules,
the scalar product is
are computed on a three-dimensional grid over the two superimposed
molecules,
the scalar product is
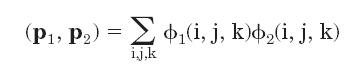
 .
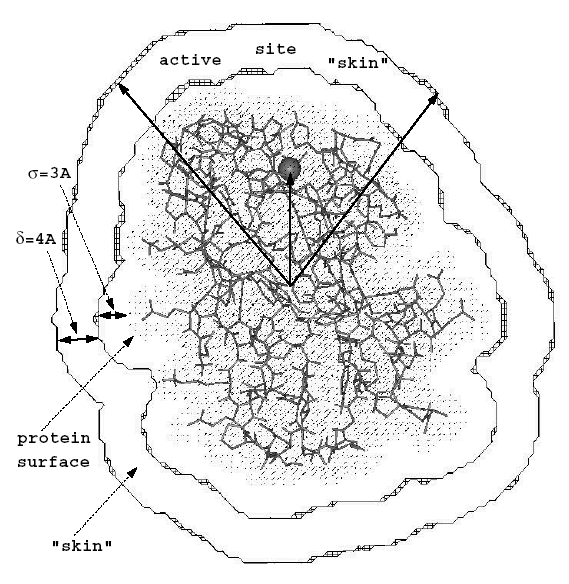
The "skin" of each molecule is defined as the volume remaining after
excluding
the region inside the surface accessible to the center of a probe with
radius
.
The "skin" of each molecule is defined as the volume remaining after
excluding
the region inside the surface accessible to the center of a probe with
radius 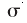 ,
and the region outside the surface accessible to a probe of radius
,
and the region outside the surface accessible to a probe of radius 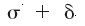 .
The "region of interest" is the intersection of the "skins"
of the two molecules.
.
The "region of interest" is the intersection of the "skins"
of the two molecules.
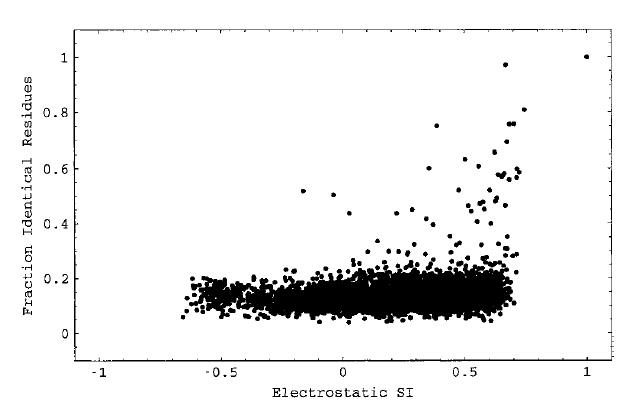
The SI analysis can be performed for the complete molecular skins or restricted to particular chosen regions of the skins, e.g. around a protein binding site. In the latter case, a vector can be chosen pointing from the center of the proteins to the region to be studied. The figure shows a blue copper protein (the copper ion represented by a sphere) with the definition of the conical region, where the potentials are compared:
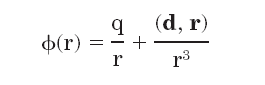
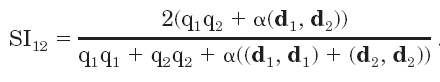
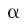 depending
on the region, where the potentials should be compared.
depending
on the region, where the potentials should be compared.