- results : 352 sequences retrieved.
2. BLAST using HTYLPPPYPG
[EMBO J, 1999, 18, 2551].
- Results: the
motif is not perfectly conserved in any of the yeast sequences.
3. PatMatch using PPPY
[J. Virology, 1999, 37, 2921]
-results:
Two proteins showing this motif could be of interest, DNA TOPOISOMERASE
I (TOP1_YEAST
) and UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME (UBC6_YEAST
).
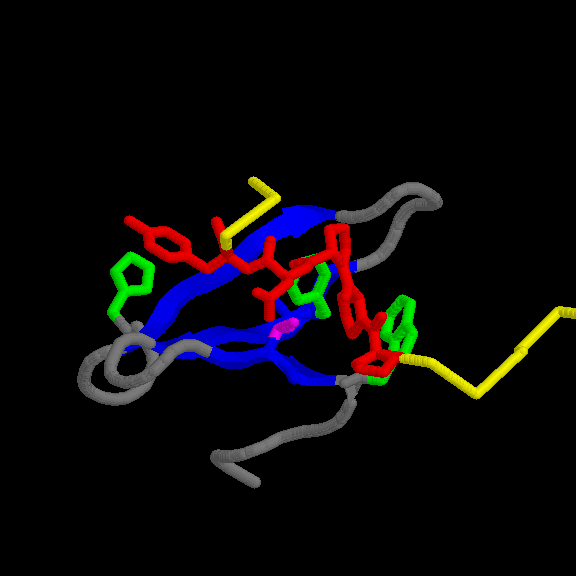
Location of the motifs in the structureDNA TOPOISOMERASE I (156-159): the 3D structure of N-terminal fragment of this protein is known (1ois ). The motif is accessible to the solvent (fig.1 and table I). Note that the Tyr side chain is not very accessible however. Its side chain does not extablish Hbonds.
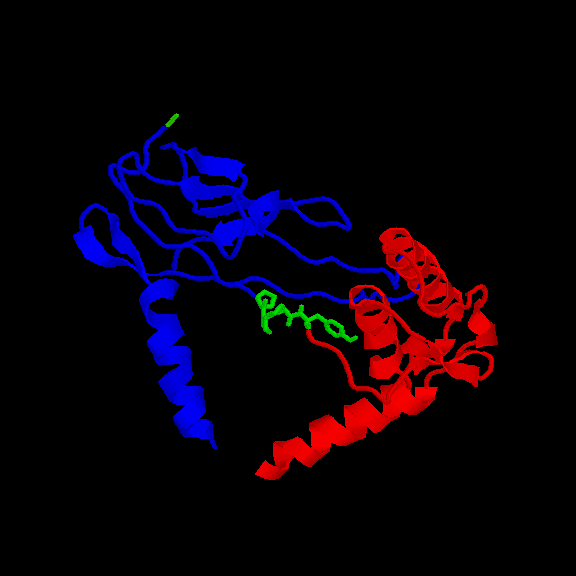
Fig. 1 Location of the PPPY motif (in green) in topoisomerase I from yeast. The protein contains two domains
represented in blue and red. The motif connects the two domains.
Table I. Acessibility of the residues in the motif (ABS=absolute, REL=relative in %)
REM RES _ NUM All-atoms Total-Side Main-Chain Non-polar All polar
REM ABS REL ABS REL ABS REL ABS REL ABS REL
RES PRO 156 26.03 19.1 18.25 15.2 7.79 48.0 18.25 15.1 7.79 51.3
RES PRO 157 104.04 76.4 100.89 84.1 3.15 19.4 100.89 83.4 3.15 20.8
RES PRO 158 104.23 76.6 95.88 80.0 8.36 51.5 95.88 79.3 8.36 55.0
RES TYR 159 67.44 31.7 48.84 27.5 18.60 52.6 46.55 34.1 20.89 27.4
Several other structures are known for topoisomerase I . In fig.2 we show the structural alignemnt of Human DNA topoisomerase in non-covalent complex with a 22 base pair DNA duplex (1a36 ) with the N-terminal fragment of the yeast enzyme. The two structures are rather similar, they also share high sequence identity in the alignment region. In yeast, binding to DNA is thus probably acompanied by minor conformational changes and the Tyr residue probably does not become more accessible upon binding as well. Binding to a ww domain could neverthless trigger larger conformational rearrangements. Those could block the function of enzyme (binding). Its is also interesting to note that the motif is quite conserved ( results )
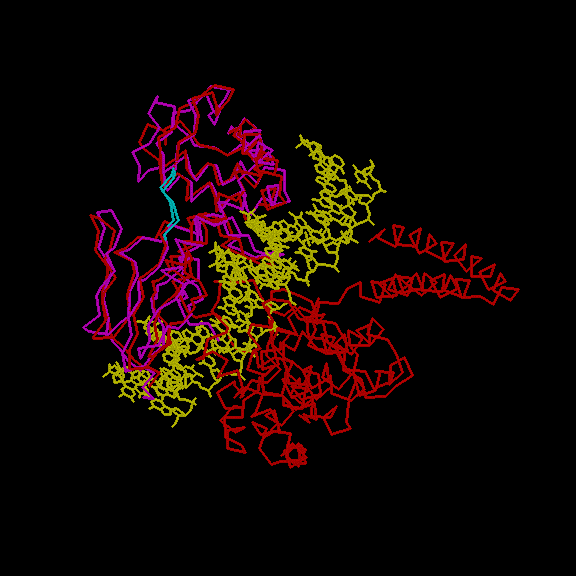
Fig. 2 (top) Fitting of N-terminal fragment of DNA topoisomerase I from yeast (mangenta) with the human DNA topoisomerase I (red) complexed with a 22 base pair DNA (yellow). The motif is shown in cyan. (bottom) detailed view of the motif.
UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME (21-24): we built a model for this protein. The WHAT_CHECK report of the model presents problems in the packing of some residues. However, those residues are not located near the motif. The overall topology of the model should be correct nevertheless since ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes have a high sequence similarity. The motif is accessible (fig. 3 and table II).

Fig. 3 Location of the PPPY motif (in green) in UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYMEREM RES _ NUM All-atoms Total-Side Main-Chain Non-polar All polar
Table II. Acessibility of the residues in the motif (ABS=absolute, REL=relative in %)
REM ABS REL ABS REL ABS REL ABS REL ABS REL
RES PRO 21 62.76 46.1 48.85 40.7 13.91 85.7 48.92 40.5 13.83 91.1
RES PRO 22 8.56 6.3 6.23 5.2 2.33 14.4 6.23 5.1 2.33 15.4
RES PRO 23 106.22 78.0 100.08 83.5 6.14 37.8 100.08 82.7 6.14 40.4
RES TYR 24 124.08 58.3 109.06 61.5 15.02 42.5 78.03 57.2 46.05 60.4
4. PatMatch analysis using different
RSP5 binding peptides according to Kasanov's results [Chem
Biol, 2001, 8, 231-241]. They defined the peptide ligand preferences
for 14 WW domains knowing to bind the group 1 motif. Among them there are
also RSP5 WW domains.
We used each peptide reported to bind RSP_1,
RSP_2, RSP_3 as seed sequence in PatMatch retrieving no yeast sequence
showing them.
4.1 PatMatch using RSP5_1 consensus [WXX(W/Y)LXPPXY].
- -Results: The consensus sequence reported
in the article shows an aromatic residue in its forth position. PatMatch
doesn't permit to select aromatic residues. Because of the occurrence in
peptides selected by this WW domain of a tryptophan or a tyrosine in this
position, we try to perform the search using both these amino acid. No
sequence has been retrieved.
Replacing these amino acid with a hydrophobic residue in this position (consensus WXXBLXPPXY) we retrieved only one sequence:
|
|
|
|
|
|
| DPOZ_YEAST |
|
WKYALKPPTY |
|
|
- - Results:
|
|
|
|
|
|
| S69014 |
|
INTPPPY |
|
|
| S65289 |
|
INTPPPY |
|
|
| S66740 |
|
INTPPPY |
|
|
| S65305 |
|
WGVPPPY |
|
|
| S66832 |
|
YPPPPPY |
|
|
| TOP1_YEAST |
|
VIFPPPY |
|
|
| UBC6_YEAST |
|
VENPPPY |
|
|
| YM95_YEAST |
|
ADEPPPY |
|
|
| YD23_YEAST |
|
VESPPPY |
|
|
* S65305 is a probable membrane protein. No domain detected by SMART. PSI-BLAST against a NRDB doesn't retrieve any homologous sequence.
* S66832 corresponds to Med7, a component of the Mediator complex responsible for transcriptional activation [Genes Dev, 1998 12, 45-54]. No domain detected by SMART.
* YM95 is a hypothetical protein with no domain detected by SMART. PSI-BLAST using all the sequence converged at the second iteration, showing high homology only with other yeast hypothetical proteins. Among these only one (CAA99717.1) shows a partial conservation of the hypothetical WW binding domain motif (VQDPPLY). The only sequence below the threshold (E=6.4, AE001746_12) is a Thermotoga maritima phosphomannomutase that shows the binding motif partially conserved (SHNPPEY).
* YD23 s a hypothetical membrane protein in which
an uncharacterized protein family domain (UPF0057)is
present (aa 11-62). This is a region shared by different, uncharacterized
proteins that have been shown to be evolutionary related [Electrophoresis
1998, 19, 536-544]. YD23 is 140 residues long and the motif is localized
just at the end of the protein. BLASTing with this sequence against NRDB,
converged at the 5th iteration retrieving all the other proteins that show
the UPF0057 domain. None of them presents the WW binding motif too.
- - Results:
- Second type: PPLP motif
|
|
|
|
|
|
| S69014 |
|
PPPYLTL |
|
|
| S65289 |
|
PPPYLAL |
|
|
| S66740 |
|
PPPYLTL |
|
|
| S66832 |
|
PPPYVKF |
|
|
| TOP1_YEAST |
|
PPPYQPL |
|
|
| UBC6_YEAST |
|
PPPYILA |
|
|
| YM8G_YEAST |
|
PPPYNDV |
|
|
| YM95_YEAST |
|
PPPYTVA |
|
|
| YN13_YEAST |
|
PPPYKLG |
|
|
* YN13 is a hypothetical protein with no domain detected by SMART. PSI-BLAST
against NRDB converged at the 5th iteration; all the sequences retrieved
don't show the motif.
- results : 12 proteins showing the exact match, 39 containing the PPPL motif and 67 containing the PPLP motif.
Analysis of the 12 exact matches1.2 Domain omposition and function
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Q06604 | Ypr171w | 186-190 | unknown | none | Conv. 2nd iteration. No homologous. |
| P53933 | Ynl094w | 507-511 | unknown | none | Conv. 3rd iteration. Only hypothetical proteins, none showing the motif. |
| P40021 | YER033C | 120-124 | unknown | none | Conv. 1st iteration. No homologous. |
| P28003 | YAL034C or FUN19 | 245-249 | unknown | none | Conv. 3rd iteration. Under threshold, only hypothetical proteins, none showing the motif.Below threshold, protein kinase PKNbeta (JC7083, E=0.041, PPPKP) |
| Q00453 | RGM1 | 155-159 | Probable transcription repressor. The Pro-rich region (95-211) is able to repress the DNA expression. | ZnF_C2H2 (19-44; 50-73 Zinc Finger domain) | |
| S64993 | YLR144C | 24-28 | Necessary for actin polymerization in permeabilized cells (Science, 1999 285, 901-6) | none | |
| P40450 | BNI1 related protein 1 | 777-781
803-807 824-828 |
Involved in microtubules organization. Potential target for RHO proteins. | FH2 (Formin Homology 2 Domain, 868-1332) | |
| P40453 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 7 | 530-537 | Hydrolysis of ubiquitin C-terminal thioester | RHOD
(Rhodanese Homology Domain 318-447)
UCH-1(Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolases 1 609-640) UCH-2 (Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolases 2 994-1068) |
|
| P32521 | PAN1 protein | 1402-1406 | Cytoskeletal adaptor (GO) | EH (Eps15 homology domain)
Efh (EF-hand, calcium binding motif) |
|
| P37370 | Verprolin | 353-357 | Involved in cytoskeletal organization and cellular growth. It can bind SH3 domain and is very rich in Pro. | WH2 (Wiskott Aldrich syndrome homology region 2/actin binding 30-47, 87-106) | |
| P41832 | BNI1 protein | 1305-1309 | Involved in microtubules organization. Potential target for RHO proteins | DNA_topoIV
(DNA gyrase/topoisomerase IV, subunit A 756-789)
FH2 (Formin Homology 2 Domain 1348-1824) |
|
| P32491 | MAP kinase (MKK2) | 88-93 | Ser/Thr protein kinase involved in a signal trasduction pathway important in yeast cell morphogenesis and growth. | S_TKc (Ser/Thr protein kinases, catalytic domain 214-481) |
1.2 Fasta search against the PDB database using the 12 proteins showing the perfect match.2. PatMatch using PPPLP motif.
results : in most of the cases the motif is outside the region of alignment, in other cases it is not 100% conserved. The results' file also contains links to SacchDB and SWISS_PROT entries for each of the 12 proteins.
- Results: Same results than using BLAST.
3. Pattern
Search against PBD for PPLP motif containing proteins.
- Results: 31 structures
retrieved. Most of them are peptides or don't show homologous when used
as seed sequences against YNRDB. No yeast homologous sequences have been
retrieved mantaining a conserved PPLP motif.
1. PatMatch using PXXGMXPP motif
-Results:
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Q05455 | PLIGMAPP | unknown | 24 | 31 |
| P45976 | PMPGMMPP | Pre-mRNA polyadenylation factor that directly interacts with poly(A)polymerase. | 306 | 313 |